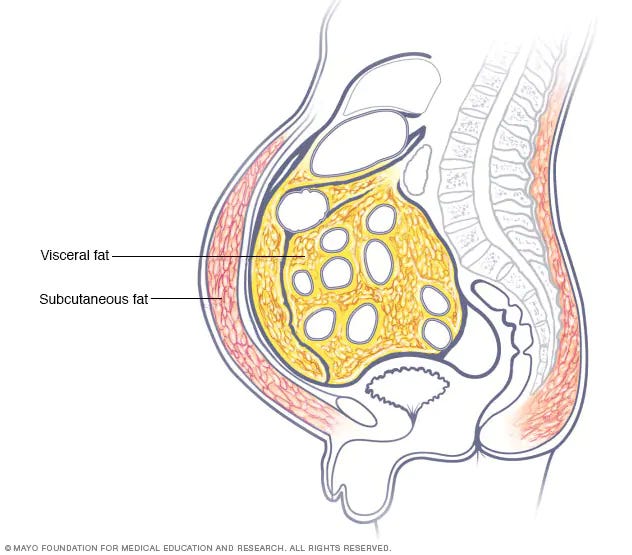
Belly fat in men is a common issue that not only affects physical appearance but also overall health. Besides its aesthetic impact, excess belly fat can be a sign of poor health. In this article, we'll explore the factors contributing to belly fat accumulation in men, associated risks, and ways to manage this problem.
What Causes Belly Fat Accumulation in Men?
Genetic Factors: Genetic predisposition can play a significant role in body fat distribution. Some individuals are more prone to accumulating fat in the abdominal area due to genetic inheritance.
Unhealthy Diet: Excessive consumption of high-calorie, saturated fat, and sugary foods can lead to increased fat deposits in the abdominal area. A diet rich in processed foods and fast food is a major contributor to abdominal obesity.
Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity and a sedentary lifestyle lead to increased fat deposits, especially in the abdominal area. Lack of exercise can slow down metabolism and promote fat accumulation.
Stress: High levels of stress can trigger the secretion of cortisol, a hormone associated with increased abdominal fat. Additionally, stress can lead to adopting unhealthy eating habits such as excessive consumption of high-calorie foods or sweets.
Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Alcohol is high in calories and can contribute to fat accumulation in the abdominal area. Excessive alcohol consumption can inhibit fat burning and promote its storage in the abdomen.
Risks Associated with Belly Fat in Men:
Cardiovascular Diseases: Excessive belly fat is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases such as hypertension, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease.
Type 2 Diabetes: Abdominal obesity is a major risk factor for developing type 2 diabetes. Abdominal fat interferes with insulin sensitivity and can lead to increased blood sugar levels.
Metabolic Conditions: Abdominal fat may also be associated with metabolic conditions such as metabolic syndrome, which includes a combination of risk factors for cardiovascular diseases and type 2 diabetes.
Mental Health Issues: Abdominal obesity can have a negative impact on self-esteem and mental health, leading to stress, depression, and anxiety.
Management Strategies for Belly Fat:
Healthy Eating: Adopting a balanced diet rich in vegetables, fruits, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help reduce belly fat. Limiting the consumption of processed foods and refined sugars is also essential.
Regular Exercise: Regular physical activity, such as cardio workouts and strength training, can help burn belly fat and improve body composition.
Stress Reduction: Adopting stress management techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing can help reduce cortisol levels and, consequently, belly fat.
Limiting Alcohol Consumption: Reducing alcohol consumption can contribute to reducing belly fat and improving overall health.
Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Maintaining a healthy weight through an active and balanced lifestyle can help prevent the accumulation of fat in the abdominal area and reduce the risk of obesity-related complications.
In conclusion, belly fat in men is not just an aesthetic issue but also a concern for overall health. Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management, can help reduce belly fat and prevent associated risks.